Content

Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. For subsequent students, change all entries to reflect inclusion of previous students’ education choice. For each education option, enter the amounts into TaxSlayer, record the Refund Monitor amounts. Test the Tuition & Fees option first since the required school information for the others will be erased when that option is chosen.
This statement helps you figure your credit. The form will have an amount in box 1 to show the amounts received during the year.
Satisfaction Guaranteed — or you don’t pay. You may use TurboTax Online without charge up to the point you decide to print or electronically file your tax return. Printing or electronically filing your return reflects your satisfaction with TurboTax Online, at which time you will be required to pay or register for the product. When you use TurboTax to prepare your taxes, we’ll handle all of these calculations for you.
You can’t claim both the American opportunity credit and the lifetime learning credit in the same year. You can still receive 40% of the American opportunity tax credit’s value — up to $1,000 — even if you earned no income last year or owe no tax. For example, if you qualified for a refund, this credit could increase the amount you’d receive by up to $1,000. That’s why the American opportunity credit is typically the best education tax break for students and their families. You can claim these education tax credits and deductions even if you paid for school with a student loan. Parents can take advantage, too, so long as they don’t choose a married filing separately status.
If the student is a dependent, go to the student’s return below and enter data from their return as well. Due to interactions with other tax benefits, this may not be the best solution but often is. Use maximum allocates all scholarship available, after any designated as taxable in the funding sources tab, to qualified expenses before diverting allowed amounts to nonqualified expenses. The optimizer uses this option as it cycles through taxable amounts. Include any required computer and internet expenses in the required supplies and equipment fees category. If not required, include it in living expenses.
By authorizing H&R Block to e-file your tax return, or by taking the completed return to file, you are accepting the return and are obligated to pay all fees when due. Offer valid for tax preparation fees for new clients only. A new client is an individual who did not use H&R Block office services to prepare his or her 2016 tax return.
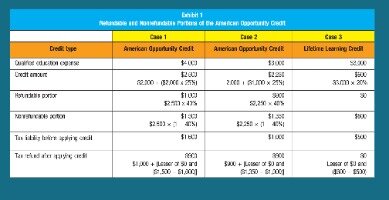
Then enter education expenses in the Expense Information tab. The columns to the right will show what expenses qualify for the American Opportunity Credit, Lifetime Learning credit, or for Tuition and Fees adjustment. A check-mark to the left of each expense catagory indicates funds that can be used for the funding amounts in the Funding Sources tab . An option in the qualified expenses row, allows you to use all available funds to be spent on the qualified expenses or to use only the amount that covers expenses over that allowed for the particular credit . The bottom two rows show the amounts that can be used in the taxpayer’s return and the amount of unused scholarship funds that are taxable. The full credit is worth 20% of up to $10,000 in eligible costs, which means the maximum credit is $2,000.
The Irs Is Accepting Returns File With Us Now To Get Your Max Refund, Guaranteed.
Visit hrblock.com/ez to find the nearest participating office or to make an appointment. OBTP#B13696 ©2017 HRB Tax Group, Inc. However, the $2,000 maximum is per return, not per student. So if you spent $5,000 on schooling for a qualified dependent, and another $5,000 on eligible education expenses for yourself, you would still be able to claim the maximum 20%, or $2,000, credit. If you spend less than $10,000, your credit isn’t worth as much. You can deduct up to $4,000 from your gross income for money you spent on eligible education expenses in tax year 2020. These expenses include tuition, fees, books, supplies and other purchases your school requires.
- Up to 40% of the American Opportunity credit is refundable up to $1,000.
- If not required, include it in living expenses.
- You can’t claim a credit for each student.
- It is better to allocate $3,000 toward qualified education expenses and the remaining $5,000 to nonqualified expenses.
- Both credits and deductions are an important component of lowering your federal tax burden each year.
- If approved, funds will be loaded on a prepaid card and the loan amount will be deducted from your tax refund, reducing the amount paid directly to you.
The lifetime learning credit is for qualified tuition and related expenses paid for eligible students enrolled in an eligible educational institution. This credit can help pay for undergraduate, graduate and professional degree courses — including courses to acquire or improve job skills. There is no limit on the number of years you can claim the credit. It is worth up to $2,000 per tax return.
If the purchase of books, supplies or equipment is necessary for enrollment, those costs may be included as well. However, the credit is largely offset by the increased tax due to the $8,000 of additional income. The net result is a tax benefit of $440 compared with the original return. However, taxpayers in states with an income tax may find the increased state tax outweighs the benefits of pursuing this strategy for the lifetime learning credit. Enrollment in, or completion of, the H&R Block Income Tax Course is neither an offer nor a guarantee of employment. Additional qualifications may be required.
What Is The Credit Worth?
Terms and conditions apply; seeAccurate Calculations Guaranteefor details. Qualified expenses for the Lifetime Learning Credit also include the cost of courses that aren’t part of a degree or certificate program. So, working adults who take occasional courses to strengthen their job skills are eligible to claim this credit. You can’t claim both credits for the same student, so you’ll need to decide which credit is best for your situation. NerdWallet strives to keep its information accurate and up to date.
Like with education tax credits, personal expenses like transportation and room and board don’t qualify for this deduction. Tax credits are based on qualified education expenses payed for the taxpayer, spouse, or a dependent who is claimed as an exemption on the tax return. Only expenses required for enrollment or attendance at the eligible institution are qualified expenses. In other words, only expenses you are contractually obligated to pay are eligible.
That maximum still applies even if you’re paying tuition costs on behalf of multiple people. For instance, if you’ve paid tuition expenses for three of your children and they each had tuition expenses of $10,000, you can still only claim $2,000 total – not $2,000 each. In order to claim the Lifetime Learning credit, either you, your spouse, or any of your dependents must be enrolled at an eligible educational institution. The American Opportunity Credit is another popular educational credit that you can claim using Form 8863. As with the LLTC, you can claim the American Opportunity Credit for yourself, your spouse or your dependents with qualifying educational expenses while pursuing an undergraduate degree. The American Opportunity Credit has a higher limit than the Lifetime Learning Credit, at $2,500, and the phase-out begins at higher MAGI levels as well. Form 8863 is a two-page form used for computing educational tax credits.

Those with MAGIs of $90,000 or $180,000, respectively, aren’t eligible to claim it. This income limit is a somewhat larger income range compared to the Lifetime Learning credit. You must reduce your qualifying expenses by the amount of any financial assistance received from grants, scholarships, or reimbursements. Still, you don’t have to reduce them if you pay college tuition using borrowed funds. This borrowing includes student loans or gifts from family members.
Married couples filing jointly qualify for the full credit with a modified adjusted gross income of $160,000 or less, and single filers qualify with an income of $80,000 or less. The credit phases out completely at $180,000 for married couples and $90,000 for single filers. was not presented to the student and how the education credits were calculated.
Nonqualified Education Expenses
The American Opportunity credit can often be greater, so taxpayers typically only claim the Lifetime Learning credit when they cannot claim the American Opportunity Credit due to its enrollment restrictions. It begins phasing out for single taxpayers with MAGIs of $80,000 and $160,000 for married couples filing jointly.
TurboTax®offers limited Audit Support services at no additional charge. H&R Block Audit Representation constitutes tax advice only. Consult your attorney for legal advice.
Of course, the offers on our platform don’t represent all financial products out there, but our goal is to show you as many great options as we can. Explore student loan refinancing and get interest rate quotes from top-ranked lenders. See 2021’s standout student loans and refinancing options. All backed by tons of nerdy research.
Ways The Irs Helps Pay For Education Via Tax
She has more than a dozen years of experience in tax, accounting and business operations. Christina founded her own accounting consultancy and managed it for more than six years. She co-developed an online DIY tax-preparation product, serving as chief operating officer for seven years. She is the current treasurer of the National Association of Computerized Tax Processors and holds a bachelor’s in business administration/accounting from Baker College and an MBA from Meredith College. Taking courses to improve your skills or to secure a graduate degree is a valuable investment, but higher education doesn’t come cheap. This article was fact-checked by our editors and Christina Taylor, MBA, senior manager of tax operations for Credit Karma Tax®. It has been updated for the 2019 tax year.
After using the calculator, consider printing a copy for the taxpayer’s records. The “Print all” button will print all but the Instructions. If you want that as well, print from this page.
This allows the student to retain $4,000 ($7,000 — $3,000) in qualified education expenses, the maximum amount allowable in calculating the American opportunity tax credit. This allocation creates a $1,900 tax benefit when compared with the original return (see the table “Student in Undergraduate and Graduate School in the Same Year”). The lifetime learning credit (“LLC” in the accompanying tables) offers a credit for 20% of up to $10,000 in qualified education expenses.
Increasing the couple’s income could decrease the EITC beyond the gains received from the increased education credits. By examining eligibility requirements and reviewing the details of your education expenses, you can better choose which tax credit provides will make the biggest difference on your tax bill.
Q&a: How Does A Tax Credit Affect My Tax Return?
But this amount may not be the amount you can claim. See qualified education expenses for more information on what amount to claim.

