Content
“Coronavirus-related relief for retirement plans and IRAs questions and answers.” Accessed Jan. 30, 2021. In addition, the CARES Act allows those affected by the coronavirus outbreak a hardship distribution of up to $100,000 without the 10% penalty those younger than 59½ normally owe. In addition, there are other events that constitute a hardship and therefore yield an exemption from the 10% penalty. They include economic challenges, such as job loss, the need to pay college tuition, or putting a down payment on a house. If retirees can afford to delay collecting Social Security benefits, they can also raise their payment by almost a third. If you were born within the years 1943–1954, for example, your full retirement age—the point at which you will get 100% of your benefits—is 66.
- We asked, and they gave us some good tips on reducing your taxable burden and avoiding the 20% mandatory withholding.
- “Some plans don’t allow loans, and some may have different repayment terms, so you have to check on your individual plan,” Rebell says.
- The last thing you want is to forgo some of your hard-earned savings because you failed to take your RMDs in time.
- An individual retirement account is a tax-advantaged account that individuals use to save and invest for retirement.
- Instead of losing a portion of your investment account forever—as you would with a withdrawal—a loan allows you to replace the money through payments deducted from your paycheck.
- And if you’ve been invested for quite some time, chances are the earnings are quite substantial.
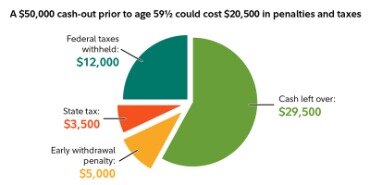
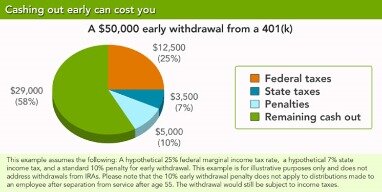
For 2020 only, you can withdraw funds from your 401 at any age and you won’t pay the early withdrawal penalty. The withdrawal’s taxes and penalties break down to 20% for federal taxes, 7% for state taxes, and a 10% early withdrawal penalty, for a total of 37%. With a 401 loan, you borrow money from your retirement savings account. Depending on what your employer’s plan allows, you could take out as much as 50% of your savings, up to a maximum of $50,000, within a 12-month period. A loan lets you borrow money from your retirement savings and pay it back to yourself over time, with interest—the loan payments and interest go back into your account. Every employer’s plan has different rules for 401 withdrawals and loans, so find out what your plan allows. This determination generally is to be made on the basis of all relevant facts and circumstances.
How To Make A 401(k) Hardship Withdrawal
Jim has run his own advisory firm and taught courses on financial planning at DePaul University and William Rainey Harper Community College. Rebell says the amount of time it takes to get your money in hand will vary by plan, so it’s better to get a head start now. Even before the pandemic many workers have needed to dip into their retirement account to make ends meet, Transamerica CEO Catherine Collinson said. It will take years for those people to recover those losses and some many never recover, she added. Here are a couple of reasons you might not want to take a 401 withdrawal. Only withdraw as much as you need and keep seeking out alternative sources of funding.
Remember, you’ll have to pay that borrowed money back, plus interest, within 5 years of taking your loan, in most cases. Your plan’s rules will also set a maximum number of loans you may have outstanding from your plan. You may also need consent from your spouse/domestic partner to take a loan. If you opt for a 401 loan or withdrawal, take steps to keep your retirement savings on track so you don’t set yourself back. Borrowing from your plan may have a negative impact on the earnings of your account and reduce the money you will eventually have available for your retirement.
K) Minimum Distributions: What You Need To Know
If, at any point, you’ve made after-tax contributions to your 401k plan, then you have the opportunity to take a withdrawal of those assets should the need arise. A defined-contribution plan is a retirement plan in which employees contribute part of their paychecks to an account intended to fund their retirements. A premature distribution is one taken from an IRA, qualified plan, or tax-deferred annuity that is paid to a beneficiary that is under age 59½.
As with anything having to do with taxes, there are rules and conditions with each, and one wrong move could trigger penalties. Account owners also were allowed up to three years to pay the tax owed on withdrawals, instead of owing it in one year. They were also given the choice to repay the withdrawal to a 401 and avoid owing any tax—even if the amount exceeded the annual contribution limit. Those who were impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 were eligible. “There are some exceptions to this rule, but if you can take advantage of this technique, you can further defer taxable income until retirement, at which point the distributions might be at a lower tax bracket .”

You’ll also miss out on what could be crucial months or years of investment returns. Another major downside of a 401 loan is that you might have to pay back the loan within 90 days if you leave your job or are terminated.
Rmd Rules For 401(k) Plans
But if you delay to age 67, you’ll get 108% of your age 66 benefit, and at age 70 you’ll get 132% . Any income needed above this amount should be withdrawn from positions with long-term capital gains in a brokerage account or Roth IRA. Then, if they are over 72, subtract their required minimum distribution. The remainder, if any, is what should come from the retirees’ 401, up to the $40,400 or $80,800 limit. Since all of your 401 distribution is based on your tax bracket at the time of distribution, only take distributions to the upper limit of your tax bracket. If you borrow from your 401 and neglect to repay the loan, the amount will be taxed as if it was a cash distribution. On March 27, 2020, President Trump signed a $2 trillion coronavirus emergency stimulus package into law, called the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act.
Let’s use the previous example of the participant with a $15,000 after tax balance in her account – $10,000 of which is principal (non-taxable) and $5,000 of which is earnings . Since the $5,000 in earnings represents one-third of the overall $15,000 balance, that means that any withdrawal she takes of after tax dollars must consist of roughly 33% in earnings.
Here’s what you need to know about 401 withdrawals and loans—plus alternatives. For more information, refer to the section, “Loans Treated as Distributions,” in Publication 575. Generally, if permitted by your plan, you may borrow up to 50% of your vested account balance up to a maximum of $50,000. The loan must be repaid within 5 years, unless the loan is used to buy your main home. The loan repayments must be made in substantially level payments, at least quarterly, over the life of the loan. A loan from your employer’s 401 plan is not taxable if it meets the criteria below.
However, once you reach 72, it’s no longer a choice to withdraw from your 401, it’s mandatory. The IRS has defined required minimum distributionsfor certain retirement accounts, including 401s. “Account holders have up to three years to pay taxes on the withdrawal. The money can also be paid back into a retirement plan within three years to help keep you on track with your retirement goals,” Murphy says. Ruedi said households that have been financially stressed due to the pandemic were likely going to take from their retirement accounts even with the penalty, but the provision makes the move a little less harmful. Taking an early withdrawal from a retirement account before age 59 1/2 isn’t a rare move for Americans.
You can now take out up to $100,000 from your retirement account without incurring this extra tax on early withdrawals. Yes, but any distribution will be taxed as ordinary income and will be subject to the 10% penalty if the person making the 401 withdrawal is under 59-1/2. A financial advisor can be a big help in putting together a retirement income plan that accounts for living expenses, taxes and other considerations. People who work with financial advisors report greater financial security, and research suggests that working with an advisor can result in additional annual investment returns ranging from 1.5% to 4%.
If you need to plan your 401 withdrawals, you should consider working with a financial advisor. While the CARES Act has increased the amount that you can borrow or withdraw and removed some penalties, you still have to pay the money back or pay taxes on your withdrawal, Murphy says. If you choose a 401k loan, you can avoid paying taxes on the money you take from your 401k, but you have to pay that money back.
Previously, RMD rules required that workers begin taking Required Minimum Distributions by April 1 of the year after the accountholder turned 70 1/2. However, the rules changed with the passage of the Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act, which was signed into law in December 2019.
Let’s look at the pros and cons of different types of 401 loans and withdrawals—as well as alternative paths. No one opens and contributes to a workplace savings account like a 401 or a 403 expecting to need their hard-earned savings before retirement. But if you find you need money, and no other sources are available, your 401 could be an option. The key is to keep your eye on the long-term even as you deal with short-term needs, so you can retire when and how you want. A 401 loan may be a better option than a traditional hardship withdrawal, if it’s available.
If your 401 distributions will put you in the lower end of one tax bracket, see if you can start distributions earlier, spreading things out and potentially dropping you into a lower bracket. As long as you start after age 59.5, you could save on your total tax bill with this method. If you’ve consulted with experts, considered your other options, and still decided to pull money from your 401k, get in touch with your retirement plan managers. If you haven’t yet filed your taxes for this year, you might still be expecting a refund this year.
The elimination of this penalty removes one of the most substantial burdens associated with taking money out of a 401 early. While raiding your retirement accounts is still be a costly proposition because you lose out on the compound interest your money would’ve earned if it stayed invested, at least you don’t incur a huge IRS bill to add insult to injury. A 401 plan is a tax-advantaged retirement account offered by many employers.
Given the tax hit and opportunity cost of early withdrawals, it’s not ideal solution. Before you commit to a penalized withdrawal, consider ifborrowing the money from your 401might be a better solution. If you need personalized input, Rebell suggests consulting with a trusted financial planner or an HR manager at your place of employment before making any moves. Rebell says you have until September 23, the CARES Act 401k withdrawal deadline, to consider a withdrawal. These required distributions are calculated based on your life expectancy, so you receive the entire balance of your 401K during your life expectancy. Your plan administrator must determine the minimum amount required to be distributed to you each year. Check out the IRS’s rules for Required Minimum Distributions to help you figure your required minimum distribution.
The CARES Act gave Americans financially hurt from the pandemic an opportunity to withdraw without penalty, but that exception ended in 2020. The government may have eased the restrictions on 401 withdrawals, but you should only take advantage of this if you absolutely need the money. That forces you to save more money per month going forward in order to afford to retire according to your original schedule. If a 401 withdrawal is the only way that you can pay your bills without taking on costly credit card debt, do it.

Remember, you don’t have to take distributions on your 401 funds at your current employer if you’re still working. However, “if you have 401s with previous employers or traditional IRAs, you would be required to take RMDs from those accounts,” saysMindy S. Hirt, CFP®, a wealth advisor with Argent Financial Group in Nashville, Tenn. “One of the best ways to keep taxes to a minimum is to do detailed tax planning each year to keep your taxable income to a minimum,” says Neil Dinndorf, CFP®, a wealth advisor at EnRich Financial Partners in Madison, Wis. For 2020, you can stay in the 12% tax bracket by keeping taxable income under $80,250.
Early 401(k) Withdrawal Rules
Whether an employee has an immediate and heavy financial need is to be determined based on all relevant facts and circumstances. Publication 575includes information to help you understand the special rules covering distributions made after the death of a participant. More information on the optional methods can be found in Publication 575, Pension and Annuity Income, and in the Form 4972 InstructionsPDF, Tax on Lump-Sum Distributions. You can use this type of plan to supplement your savings for future non-retirement-related expenses, such as college tuition or an emergency fund.
You will still owe taxes on your withdrawals, unless the money comes from a Roth 401. However, the rules surrounding taxes on retirement withdrawals are also different this year. Your retirement savings is your money after all, so you can use it however you choose. But while the government has changed the rules surrounding 401 withdrawals this year, that doesn’t mean you don’t pay a price for taking one.
Weigh the following pros and cons of 401 withdrawals to decide if it’s the right move for you. A withdrawal permanently removes money from your retirement savings for your immediate use, but you’ll have to pay extra taxes and possible penalties. A 401 plan may allow you to receive a hardship distribution because of an immediate and heavy financial need. The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 mandated changes to the 401 hardship distribution rules.

