
After correcting the adjusted trial balance, we create the post-closing trial balance with only permanent accounts (assets, liabilities, equity). When preparing a trial balance at the end of an accounting period, we transfer amounts from temporary to permanent accounts. The equality of the two totals in the trial balance does not necessarily mean that the accounting process has been error-free.
If the difference is divisible by 9, you may have made a transposition error in transferring a balance to the trial balance or a slide error. A transposition error occurs when two digits are reversed in an amount (e.g. writing 753 as 573 or 110 as 101). A slide error occurs when you place a decimal point incorrectly (e.g. $ 1,500 recorded as $ 15.00). Thus, when a difference is divisible by 9, compare the trial balance amounts with the general ledger account balances to see if you made a transposition or slide error in transferring the amounts.
A trial balance can be used to detect any mathematical errors that have occurred in a double entry accounting system. Companies initially record their business transactions in bookkeeping accounts within the general ledger. Furthermore, some accounts may have been used to record multiple business transactions. Preparing an
unadjusted trial balance is the fourth step in the accounting
cycle. A trial balance is a list of all accounts
in the general ledger that have nonzero balances. A trial balance
is an important step in the accounting process, because it helps
identify any computational errors throughout the first three steps
in the cycle.
Error
As
you see in step 6 of the accounting cycle, we create another trial
balance that is adjusted (see
The Adjustment Process). It is also important to note that even when the trial balance is considered balanced, it does not mean there are no accounting errors. For example, the accountant may have failed to record an account or classified a transaction incorrectly. These are accounting errors that would not show up in the trial balance. According to a study from Indiana University, roughly 60% of accounting errors come from basic bookkeeping mistakes. You can prevent many of these mistakes by relying on a trial balance to keep track of your financial transactions.
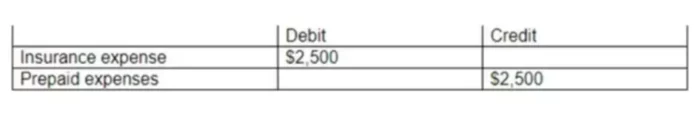
It is a record of day-to-day transactions and can be used to balance a ledger by adjusting entries. For example, Cash has a final balance of $24,800 on the debit
side. This balance is transferred to the Cash account in the debit
column on the unadjusted trial balance. Accounts Payable ($500), Unearned Revenue ($4,000), Common Stock
($20,000) and Service Revenue ($9,500) all have credit final
balances in their T-accounts. These credit balances would transfer
to the credit column on the unadjusted trial balance. An unadjusted trial balance is done before adjusting journal entries are completed.
Resources for Your Growing Business
A trial balance is a listing of the ledger accounts and their debit or credit balances to determine that debits equal credits in the recording process. Preparing and adjusting trial balances aid in the preparation of accurate financial statements. Although you can prepare a trial balance at any time, you would typically prepare a trial balance before preparing the financial statements. A trial balance is a list of all the balances in the nominal ledger accounts. It serves as a check to ensure that for every transaction, a debit recorded in one ledger account has been matched with a credit in another. If the double entry has been carried out, the total of the debit balances should always equal the total of the credit balances.
- However, this does not mean that there are no errors in a company’s accounting system.
- Preparing a trial balance regularly helps a business in spotting errors in its books.
- There are no special conventions about how trial balances should be prepared, and they may be completed as often as a company needs them.
- These next steps in the accounting cycle are covered
in
The Adjustment Process. - Once a book is balanced, an adjusted trial balance can be completed.
- BILL integrates with today’s best accounting software systems while providing innovative solutions for today’s top-performing industries.
Finding discrepancies like this is why you created a trial balance, and discovering the error now can save you time and headaches later on. You’ll record your credit balances in the center column (the credit column), while your debit balances are recorded in the far right column (the debit column). The total credit balance will appear at the bottom of the columns.
Companies can use a trial balance to keep track of their financial position, and so they may prepare several different types of trial balance throughout the financial year. A trial balance may contain all the major accounting items, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, expenses, gains, and losses. The trial balance is now ready for use in the preparation of financial statements. It is the trial balance after the company has made all the required corrections to the unadjusted trial balance.
How Do You Prepare a Trial Balance?
At the end of an accounting period, the accounts of asset, expense, or loss should each have a debit balance, and the accounts of liability, equity, revenue, or gain should each have a credit balance. On a trial balance worksheet, all of the debit balances form the left column, and all of the credit balances form the right column, with the account titles placed to the far left of the two columns. Preparing a trial balance for a company serves to detect any mathematical errors that have occurred in the double entry accounting system. If the total debits equal the total credits, the trial balance is considered to be balanced, and there should be no mathematical errors in the ledgers. However, this does not mean that there are no errors in a company’s accounting system.
Record credit and debit balances on your trial balance
Now that the debit and credit totals match at $101,000, the trial balance is in balance, and we can proceed to the next steps of the accounting cycle. A trial balance does not prove that all transactions have been recorded correctly or that the ledger is correct. It is simply a check to ensure that for every debit entry, a corresponding credit entry has been made.
Balance Method
If the outcome of the difference
is a whole number, then you may have transposed a figure. For
example, let’s assume the following is the trial balance for
Printing Plus. The right accounting or invoicing platform can minimize errors caused by manual data entry. Advanced AI can even pull financial data straight from your invoices and other documents, and this automation increases your efficiency while boosting your overall accuracy. Limitations aside, a trial balance can still be a valuable tool for evaluating your company’s finances, and it can be helpful when you examine your company’s financial statements.
If you’re preparing your trial balance with a spreadsheet software program like Microsoft Excel, you can insert a formula that will perform the calculation for you. While a trial balance can provide a helpful snapshot of your financial position, it’s not a foolproof method of preventing all possible mistakes. Even if your debit and credit entries add up to zero, that doesn’t mean they are correct.

