Content
By authorizing H&R Block to e-file your tax return, or by taking the completed return to file, you are accepting the return and are obligated to pay all fees when due. H&R Block online tax preparation and Tax Pro Review prices are ultimately determined at the time of print or e-file. All prices are subject to change without notice. Prices based on hrblock.com, turbotax.com and intuit.taxaudit.com (as of 11/28/17).

The income from RSU vesting and the associated tax withholdings are already included on your W-2, and you just use those numbers as-is. RSU stands for Restricted Stock Units. It’s the new form of stock-based compensation that has gained popularity after the employers are required to expense employee stock options. The biggest difference between RSUs and employee stock options is that RSUs are taxed at the time of vesting while stock options are usually taxed at the time of option exercise. The employer is required to withhold taxes as soon as the RSUs become vested. If one had 130 RSUs and 45 were sold to cover the tax amount then what would one list for the Cost Basis on the tax form? The cost of all 130 at the sale price or the cost of the 45 at the sale price?
However, taxes were withheld at the time of the sale, and the gain shows up on my W2. If I show the sale and cost basis on my tax form, it’s going to look like I made this money 2x. I assume I have to report it, but I’m not sure how.
This income is added to your W-2 and taxed with your wages. These stock awards to employees are different than restricted shares that securities laws prohibit the owners from selling.
At that point, you have to report income based on the fair market value of the stock. A restricted stock unit is a substitute for an actual stock grant. If your company gives you an RSU, you don’t actually receive company stock. Rather, you receive units that will be exchanged for actual stock at some future date. Typically, the date you take ownership of the actual shares, known as the vesting date, is based on either time or performance. Among the biggest risks in holding RSU shares is overexposure to your own company. Since your company pays your salary, you are already susceptible to changes in your company’s performance.
Download Our Freestock Comp Glossary App!
Think when you get a cash bonus, which the employer is required to withhold at a higher rate. If it turns out to be too high, you get the difference back when you file your taxes.
@Stan – The case you described is called “net issuance.” I will add it to the post shortly. In net issuance, you never see the sale. You were promised 100 shares but you only receive 60 shares upon vesting. If you do an entry on Schedule D, it’s going to be zero anyway. Just make a note of the price for your 60 shares. When you sell your 60 shares later, the price difference will be your capital gain or loss.
Restricted Stock Awards And Tax
The vesting schedule can also be performance-based, e.g., tied to company-specific or stock-market targets. Restricted stock units are a way your employer can grant you company shares. One of the tricky things is that you probably have the value of the vested shares and withheld taxes already on your W-2. You can make an election on your tax return and with your company to have tax assessed in the year RSUs are granted, rather than upon vesting. This is called a Section 83 election. Income tax is assessed on the fair market value of the stock on the vesting date minus any amount you paid for grant of the stock.

I think I was just confused since my basis for RSUs were based only the net shares received whereas for my stock options my basis was based on the total number of shares. The difference seems to be that the sales proceeds for RSUs were also based on the net shares and for the stock options based on the total number of shares. Belinda – The extra bit of $$ you paid out of pocket has nothing to do with the cost basis of either the shares sold or the shares remaining. Think of it as just extra withholding from your regular paycheck. You will get it back as tax refund if it turns out you paid too much tax. Turbo Tax Premier is subtracting the value of shares with held to pay taxes from my cost basis .
Valid at participating locations only. This course is not open to any persons who are currently employed by or seeking employment with any professional tax preparation company or organization other than H&R Block.
Things To Know About Your Restricted Stock Units
A four-year time-based is more common, where you’re rewarded for staying with the company for the determined time of the RSUs. Most of the potential mishaps, presented below, concern the reporting of stock sales on Form 8949 and Schedule D. I have another related question – My employer issues dividends in the form of “restricted stock” equivalent and I received 1099-DIV from the brokerage house.
The content is developed from sources believed to be providing accurate information. The information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. Some of this material was developed and produced by Advisor Launchpad to provide information on a topic that may be of interest. Advisor Launchpad is not affiliated with the named representative, broker-dealer, state- or SEC-registered investment advisory firm. The opinions expressed and material provided are for general information, and should not be considered a solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security.
In our example, although your employer says you have 100 shares vested, you actually only receive 60 shares. Follow the instructions on the bottom of Schedule D to determine your total gain or loss from the sale of your capital property. This procedure differs according to the property sold and whether you had a capital gain or loss. Complete the remaining calculations on Form 8949 to determine your total gain or loss from the sale of your RSUs. Include the sale of any other capital property in this form. Look at the 1099-B you received to report the sale of the RSUs. If there’s an amount listed in Box 3, check “Box A” on Form 8949.

On the grant date, these RSUs have no value. At the end of Year 1, a third of the stocks or 200 RSUs vests and become actual stocks.
When Is The Best Time To Sell Your Restricted Stock Units?
The vesting value for 2007 had already been account for on my 2007 W2. Thanks for the clear, concise description of tax handling for RSUs. Had to deal with this for the first time this year, and your writeup was a life saver. The RSU related income and tax withholdings are already included in your W-2.
- If you’re not satisfied, return it within 60 days of shipment with your dated receipt for a full refund (excluding shipping & handling).
- Your Confirmation of Release statement should list this amount.
- Fees apply for approved Money in Minutes transactions funded to your card or account.
- This income will be reported in box 1 of yourForm W-2and is subject to ordinary income tax.
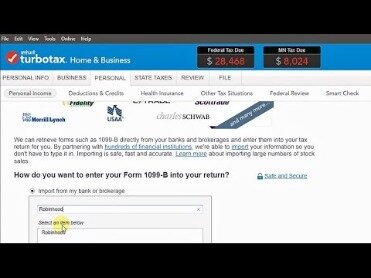
- I suggest that you either say YES to that question so TurboTax doesn’t modify your W-2 or not use the RSU section altogether and just enter 3 regular investment sales instead.
- Because of our extensive experience with these types of clients, we have seen many variations and scenarios of how the tax effects ultimately are shown on your return.
This is great if you’re charitably inclined and would otherwise donate, and comes with an additional tax benefit. Exchange Fund Strategy – If your goal is to diversify your concentrated position but you’d rather not sell your shares and incur capital gains taxes, you can opt for an exchange fund strategy. This strategy allows you to pool your stock with other large positions to offer diversification to the group. In exchange for your large number of company shares, you are given shares of the overall fund that typically comprises 50 different stock positions. In most cases, your company will handle the taxes on your behalf, by withholding taxes automatically.
Even if I think I have a “net issuance” should I treat as “sell to cover” and put a 0-gain sale on my Schedule D? I’m not sure what the IRS would think of reporting a sale that was not reported to them…. I like the deconstructed portfolio example, very eloquent. However, you didn’t directly answer whether this is a double taxation. It appears to be, since the bonus portion is taxed on the W-2 and then separately your gain on sale of your investment is taxed on the Sched D. Ashley – If your company doesn’t use a broker and you have zero gain or loss, I think you will be OK with not entering anything.
The difference must be reported by the shareholder as ordinary income. Even though you never purchased the stock, your tax basis for reporting the stock sale in column on Form 8949 is the amount of compensation income at vesting that appeared on your W-2 .
Basically you treat those shares as if you bought them at the price your company calculated on your W-2. That’s why I said you must remember the value of those remaining shares at the time of vesting until you sell them. You will show a short-term or long-term gain or loss for these shares depending on your date of sale and the sale price.
Visit hrblock.com/ez to find the nearest participating office or to make an appointment. OBTP#B13696 ©2017 HRB Tax Group, Inc. While there is no value to the employee when the RSU are issued, when the RSU is distributed, it’s another story. Once distributed, the recipient of the RSU is taxed on the value of the shares at the time of vesting. You will have the fair market value of the RSUs included as taxable wages on your Form W-2. There are many types of stock compensation, and each has its own set of rules and regulations. Executives that receive stock options face a special set of rules that restrict the circumstances under which they may exercise and sell them.

