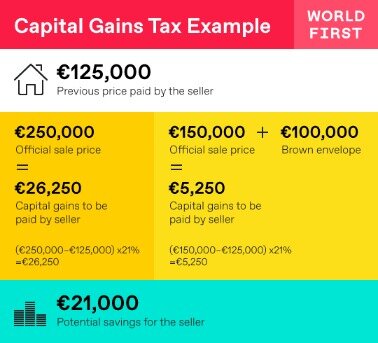
Content
When you sell your primary residence, $250,000 of capital gains (or $500,000 for a couple) are exempted from capital gains taxation. This is generally true only if you have owned and used your home as your main residence for at least two out of the five years prior to the sale. Most states tax capital gains according to the same tax rates they use for regular income. So, if you’re lucky enough to live somewhere with no state income tax, you won’t have to worry about capital gains taxes at the state level. Depending on your regular income tax bracket, your tax rate for long-term capital gains could be as low as 0%. Even taxpayers in the top income tax bracket pay long-term capital gains rates that are nearly half of their income tax rates. That’s why some very rich Americans don’t pay as much in taxes as you might expect.
In the long run, the country that has borrowed some money and has a debt, usually has to pay this debt for example by exporting some products abroad. In 1982, the U.S. owned $147 billion of assets that were excess over and above the value of U.S. assets owned by foreigners. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act puts more people into the 20% long-term capital gains tax bracket. They fall into that section when the IRS adjusts the income tax brackets each year to compensate for inflation. If you realized a gain from qualified small business stock that you held for more than five years, you generally can exclude one-half of your gain from income. You can get the specifics on gains on qualified small business stock in IRS Publication 550.
This means that focus was moved from capital to individuals and their level of income. This system also introduced a deductible allowance equal to the share’s acquisition value times the average rate for Treasury bills with a 3-month period adjusted for tax. Shielding interest shall secure financial neutrality in that it returns the taxpayer what he or she alternatively would have achieved in a safe, passive capital placement exempt from additional taxation. The main purpose of the allowance is to prevent adverse shifts in investment and corporate financing structure as a result of the dividend tax. According to the papers explaining the new policy, a dividend tax without such shielding could push up the pressures on the rate of return on equity investments and lead Norwegian investors from equities to bonds, property etc. The Working Group’s chairman Cullen claimed that the capital gains tax would raise NZ$8.3 billion over the next five years, which would be invested into increased social security benefits. In mid-April 2019, the Coalition government announced that it would not be implementing a capital gains tax, citing the inability of members of the governing coalition to reach a consensus on capital gains taxation.
Avoid Paying Capital Gains Taxes By Donating Your Stocks
Realizing the gain earlier might serve to bump you out of a “no-pay” bracket and cause you to incur a tax bill on the gains. Taking money out of the plan at retirement means you’ll likely be in a lower tax bracket.
Losses on your investments are first used to offset capital gains of the same type. For example, short-term losses are first deducted against short-term gains, and long-term losses are deducted against long-term gains. If your losses exceed your gains, you can deduct the difference on your tax return, up to $3,000 per year ($1,500 for those married filing separately), but they are not considered a regular itemized deduction. If your net loss is greater than the maximum allowed amount, you can carry the excess amount over to future tax years. For residents of Estonia all capital gains are taxed the same as regular income, the rate of which currently stands at 20%.
They can also declare losses on hard assets if they weren’t for personal use. Capital losses, either short- or long-term, can offset short- and long-term gains. The IRS looks at the total of your capital gains when calculating tax, which means your losses can offset some of the gains and soften the hit a bit.
To use this strategy, the taxpayer must specify at the time of a sale which lot is being sold (creating a “contemporaneous record”). On brokerage websites, a “Lot Selector” may let the taxpayer specify the purchase to which a sell order corresponds. In contrast, when a business is entitled to a depreciation deduction on an asset used in the business (such as for each year’s wear on a piece of machinery), it reduces the cost basis of that asset by that amount, potentially to zero. The reduction in basis occurs whether or not the business claims the depreciation. An example of an exception is the exemption from U.S. federal income tax for a limited amount of foreign earned income of a citizen or resident of the United States who is living abroad, under 26 U.S.C.§ 911. The most advantageous let gains accumulate in the account without taxes; however, taxes may be owed when the taxpayer withdraws funds from the account. For higher rate taxpayers, the rate is 28% on profits from residential property, and 20% on everything else.
An exception is when the amount of the gain happens to push you into a higher marginal tax bracket. You probably know that, if you sell your home, you may exclude up to $250,000 of your capital gain from tax. Also, unmarried people who jointly own a home and separately meet the tests described below can each exclude up to $250,000. If you sell your home, you may exclude up to $250,000 of your capital gain from tax — or up to $500,000 for married couples.
2021 Capital Gains Tax Rates
Capital gains and losses are classified as long term if the asset was held for more than one year, and short term if held for a year or less. Short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income at rates up to 37 percent; long-term gains are taxed at lower rates, up to 20 percent. Taxpayers with modified adjusted gross income above certain amounts are subject to an additional 3.8 percent net investment income tax on long- and short-term capital gains. Capital gains taxes vary depending on whether the asset in question was held for more or less than one year. If it was held for less than one year, then any capital gains realized on the sale of the asset would be taxed at the investor’s ordinary income tax rate. If on the other hand they were held for more than one year, then the capital gains would be taxed at either a 0%, 15%, or 20% tax rate. The exact tax rate chosen would depend on the overall income level of the investor, with higher-incomes associated with higher tax rates.
However, this lower rate may take different forms, including deductions or credits that reduce the effective tax rate on capital gains. However, the rules differ for investment property, which is typically depreciated over time.
What Is A Capital Gains Tax?
A taxpayer can designate that a sale of corporate stock corresponds to a specified purchase. For example, the taxpayer holding 500 shares may have bought 100 shares each on five occasions, probably at a different price each time. The individual lots of 100 shares are typically not held separate; even in the days of physical stock certificates, there was no indication which stock was bought when. If the taxpayer sells 100 shares, then by designating which of the five lots is being sold, the taxpayer will realize one of five different capital gains or losses. The taxpayer can maximize or minimize the gain depending on an overall strategy, such as generating losses to offset gains, or keeping the total in the range that is taxed at a lower rate or not at all. For individuals, the most significant exemption is the principal family home when not used for business purposes such as rental income or home-based business activity. The sale of personal residential property is normally exempt from capital gains tax, except for gains realized during any period in which the property was unused as a personal residence or portions attributable to business use.
- The same applies if you are in a higher tax bracket rather than a lower one.
- The Hong Kong taxation of capital gains on employee shares or options that are subject to a vesting period, is at odds with the treatment of unrestricted shares or options which are free of capital gains tax.
- However, the rules differ for investment property, which is typically depreciated over time.
- The tax rates for long-term capital gains are consistent with the trend to capital gains being taxed at lower rates than individual income, as this table demonstrates.
These gains are not added to other income but are taxed separately. Payment of immovable property tax is paid by both individuals and companies on property owned in Cyprus. Since the 2013 budget, interest can no longer be claimed as a capital gain. There is no capital gains tax on equity instruments traded on the BSE. Taxpayers can declare capital losses on financial assets, such asmutual funds,stocks, or bonds.
Here are the details on capital gains rates for the 2020 and 2021 tax years. There’s an additional 3.8% surtax on net investment income that you might have to pay on top of the capital gains tax. Which tax rate applies to your long-term capital gains depends on your taxable income. To correctly arrive at your net capital gain or loss, capital gains and losses are classified as long-term or short-term. Generally, if you hold the asset for more than one year before you dispose of it, your capital gain or loss is long-term. If you hold it one year or less, your capital gain or loss is short-term.

Capital gains of individual taxpayers are tax free if the taxpayer owned the asset for at least three years. If not, gains on sales of real estate and securities are absorbed into their personal income tax base and taxed at 13% and 30% (non-residents).
This tax treatment is often called the “hedge-fund loophole”, even though it is private equity funds that benefit from the treatment; hedge funds usually do not have long-term gains. It has been criticized as “indefensible” and a “gross unfairness”, because it taxes management services at a preferential rate intended for long-term gains.
For individuals, a net loss can be claimed as a tax deduction against ordinary income, up to $3,000 per year ($1,500 in the case of a married individual filing separately). Any remaining net loss can be carried over and applied against gains in future years. However, losses from the sale of personal property, including a residence, do not qualify for this treatment.

