Content

But, the court decided in favor of the local government, which took your property and paid you an amount fixed by the court. This is a condemnation of private property for public use. If you are not personally liable for repaying the debt secured by the transferred property, the amount you realize includes the full debt canceled by the transfer. The full canceled debt is included even if the fair market value of the property is less than the canceled debt. You cannot deduct any loss from abandonment of your home or other property held for personal use only. If the abandoned property is secured by debt, special rules apply.
When you sell these certificates, you usually realize capital gain or loss. For information on the sale of stock, see chapter 4 in Pub. If you deducted the costs of a property under the de minimis safe harbor for tangible property, then upon its sale or disposition, this property is not treated as a capital asset under section 1221. This election does not apply to any gain treated as ordinary income, or attributable to real property, or an intangible asset, that is not an integral part of an enterprise zone business. You may be able to exclude from your gross income 50% of your gain from the sale or exchange of qualified small business stock you held more than 5 years. The exclusion can be up to 75% for stock acquired after February 17, 2009, and up to 100% for stock acquired after September 27, 2010.
Report the exchange of like-kind property, even though no gain or loss is recognized, on Form 8824, Like-Kind Exchanges. The instructions for Form 8824 explain how to report the details of the exchange. You exchanged real estate held for investment with an adjusted basis of $25,000 for other real estate held for investment. The basis of your new property is the same as the basis of the old property ($25,000). If you buy the replacement property after you file your return reporting your election to postpone reporting the gain, attach a statement to your return for the year in which you buy the property.

May not be drawn on in the absence of a default in the transferee’s obligation to transfer the replacement property to you. However, solely for purposes of whether a person is a disqualified person as your agent, the following services for you are not taken into account. You must include in income any interest that you receive and, if the loan is a below-market loan, you must include in income any imputed interest. The due date, including extensions, for your tax return for the tax year in which the transfer of the property given up occurs. Do not treat property incidental to a larger item of property as separate from the larger item when you identify replacement property. Property is incidental if it meets both the following tests.
Turbotax Guarantees
You can contact us using this form day or night, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. You will hear back from one of our attorneys the same day or next day. Thank you dearly for taking the time to go through in great detail options for our situation.
The total paid in the sale of the assets of Company SKB is $21,000. No cash or deposit accounts or similar accounts were sold. The company’s U.S. government securities sold had a fair market value of $3,200.
The property may be taken by the federal government, a state government, a political subdivision, or a private organization that has the power to legally take it. The owner receives a condemnation award in exchange for the property taken. A condemnation is like a forced sale, the owner being the seller and the condemning authority being the buyer. This publication explains the treatment of a gain or loss from a condemnation or disposition under the threat of condemnation.
The straight line method is applied without any basis reduction for the investment credit. The useful life and salvage value you would have used to figure straight line depreciation are the same as those used under the depreciation method you actually used. If your section 1250 property becomes section 1245 property because you change its use, you can never again treat it as section 1250 property. Stored materials that vary in composition, size, and weight are not fungible.
If you sell or exchange property for less than fair market value with the intent of making a gift, the transaction is partly a sale or exchange and partly a gift. You have a gain if the amount realized is more than your adjusted basis in the property. However, you do not have a loss if the amount realized is less than the adjusted basis of the property. If you sell real property under a sales contract that allows the buyer to return the property for a full refund and the buyer does so, you may not have to recognize gain or loss on the sale. If the buyer returns the property in the year of sale, no gain or loss is recognized. This cancellation of the sale in the same year it occurred places both you and the buyer in the same positions you were in before the sale.
Gain Or Loss
Gains or losses recognized in a partial disposition of a MACRS asset. The disposition of capital assets not reported on Schedule D. If you inherit property, you are considered to have held the property longer than 1 year, regardless of how long you actually held it. For a disposition of an interest in, or property used in, a passive activity, complete Form 8582, Passive Activity Loss Limitations. For a disposition of an interest in, or property used in, an activity to which the at-risk rules apply, complete Form 6198. In the absence of an agreement, the allocation should be made by taking into account the appropriate facts and circumstances. These include, but are not limited to, a comparison between the depreciable property and all the other property being disposed of in the transaction.
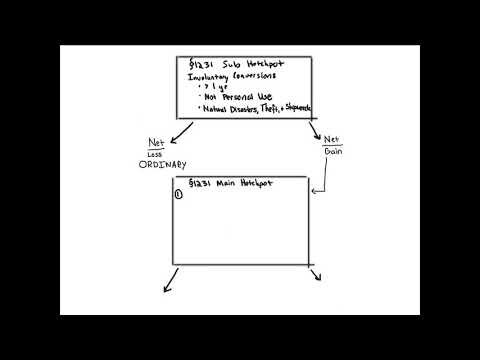
When sold, these assets must be classified as capital assets, depreciable property used in the business, real property used in the business, or property held for sale to customers, such as inventory or stock in trade. The gain or loss on each asset is figured separately. The sale of capital assets results in capital gain or loss. The sale of real property or depreciable property used in the business and held longer than 1 year results in gain or loss from a section 1231 transaction . The sale of inventory results in ordinary income or loss. Special rules apply for condemned real property used in a business or investment.
The taxpayer has this property involuntarily converted. In the conversion, the taxpayer receives compensation in the form of $1 million in cash. The taxpayer receives these funds during the month of October upon property conversion. At the close of the tax year, this taxpayer has two years to acquire similar property in order to defer the gain associated with the converted property. When a government entity forcibly takes a property from a private citizen, this taking is lawful. Lawful, that is, as long as that private citizen receives adequate compensation.
Let’s start the discussion with Treasury Regulation 1.165-6, which states that the loss of a prospective crop through frost, storm, flood or fire does not give rise to a casualty loss deduction. A cash basis farmer would not have basis in the prospective crop to claim a loss.
Definition Of Involuntary Conversion
If R pays $800,000 for his new property, R’s basis in the replacement property is $760,000 ($800,000 − $40,000). The ordinary income not reported for the year of the disposition is carried over to the depreciable real property acquired in the like-kind exchange or involuntary conversion as additional depreciation from the property disposed of. Further, to figure the applicable percentage of additional depreciation to be treated as ordinary income, the holding period starts over for the new property. You manufacture and sell steel cable, which you deliver on returnable reels that are depreciable property. Customers make deposits on the reels, which you refund if the reels are returned within a year.

A short-term loss you carry over to the next tax year is added to short-term losses occurring in that year. A long-term loss you carry over to the next tax year is added to long-term losses occurring in that year. A long-term capital loss you carry over to the next year reduces that year’s long-term gains before its short-term gains. Combine your short-term capital gains and losses, including your share of short-term capital gains or losses from partnerships, S corporations, and fiduciaries and any short-term capital loss carryover. The result is your net short-term capital gain or loss. However, taking possession of real property under an option agreement is not enough to start the holding period.
If you sold it on January 2, 2019, the holding period is exactly 192 full months. The applicable percentage for additional depreciation is 8%, or 100% minus 1% for each full month the property was held over 100 full months. The term renewal period means any period for which the lease may be renewed, extended, or continued under an option exercisable by the lessee. However, the inclusion of renewal periods cannot extend the lease by more than two-thirds of the period that was the basis on which the actual depreciation adjustments were allowed. Additional depreciation includes all depreciation adjustments to the basis of section 1250 property whether allowed to you or another person .
- Some agreements that seem to be leases may really be conditional sales contracts.
- Show any section 1231 gains and losses in Part I. Carry a net gain to Schedule D as a long-term capital gain.
- On January 1, 2019, the timber had a fair market value of $350 per MBF.
- Both the buyer and seller involved in the sale of business assets must report to the IRS the allocation of the sales price among section 197 intangibles and the other business assets.
- No gain or loss is recognized on a transfer of property from an individual to a spouse, or a former spouse if incident to divorce.
It consisted of machinery worth $30,000 and nondepreciable property worth $20,000. You received an insurance payment of $40,000 and immediately used it with $10,000 of your own funds (for a total of $50,000) to buy machinery with a fair market value of $15,000 and nondepreciable property with a fair market value of $35,000. The adjusted basis of the destroyed machinery was $5,000 and your depreciation on it was $35,000. You choose to postpone reporting your gain from the involuntary conversion. You must report $9,000 as ordinary income from depreciation arising from this transaction, figured as follows. Janet Smith owned depreciable property that, upon her death, was inherited by her son. No ordinary income from depreciation is reportable on the transfer, even though the value used for estate tax purposes is more than the adjusted basis of the property to Janet when she died.
If there are two first days of a month that are equally close to the middle of the year, use the earlier date. The holding period of a separate element placed in service before the entire section 1250 property is finished starts on the first day of the month that the separate element is placed in service. Ten percent of the unadjusted basis of the property at the start of the period determined in . The holding period used to figure the applicable percentage for low-income housing generally starts on the day after you acquired it. For example, if you bought low-income housing on January 1, 2003, the holding period starts on January 2, 2003.
On your 2019 tax return, you elect to treat the cutting of the timber as a sale or exchange. You report the difference between the FMV and your adjusted basis for depletion as a gain. This amount is reported on Form 4797 along with your other section 1231 gains and losses to figure whether it is treated as capital gain or as ordinary gain. Gain or loss on the sale or exchange of amortizable or depreciable intangible property held longer than 1 year is a section 1231 gain or loss. The treatment of section 1231 gain or loss and the recapture of amortization and depreciation as ordinary income are explained in chapter 3. 535, Business Expenses, for information on amortizable intangible property and chapter 1 of Pub. 946, How To Depreciate Property, for information on intangible property that can and cannot be depreciated.
Taxlink
If you plan to purchase replacement property with conversion compensation you have two years to do so and must recognize a gain or loss on the property where applicable within that timeframe. Different rules may apply to the allocation of the amount realized on the sale of a business that includes a group of assets. The basis of the replacement low-income housing property was its $90,000 cost minus the $51,600 gain you postponed, or $38,400. The $14,932 ordinary gain you did not report is treated as additional depreciation on the replacement property. If you sold the property in 2019, your holding period for figuring the applicable percentage of additional depreciation to report as ordinary income will have begun December 2, 1994, the day after you acquired the property. You immediately spent $105,000 of the insurance payment for replacement machinery and $9,000 for stock that qualifies as replacement property and you choose to postpone reporting the gain. $114,000 of the $117,000 insurance payment was used to buy replacement property, so the gain that must be included in income under the rules for involuntary conversions is the part not spent, or $3,000.

