Content
The American Family Act also provides the benefit for higher-income earners. Individuals who earn up to $150,000 and married couples filing jointly who earn up to $200,000 can qualify. Additionally, the bill proposes indexing the credit to inflation so that it will not be diminished over time. “It is an historic proposal in terms of lowering child poverty,” says Chuck Marr, director of federal tax policy at the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. If it were to become permanent, it would be a “landmark achievement,” he says. In the latest stimulus package, Democrats are moving ahead with plans to provide American families with $3,000 per school-aged child over the year next.
The Child Tax Credit is designed to give an income boost to the parents or guardians of children and other dependents. It only applies to dependents who are younger than 17 as of the last day of the tax year. The credit is worth up to $2,000 per dependent for tax years 2020 and 2021, but your income level determines exactly much you can get.
This, too, would boost the economy, and it would help millions of people while encouraging and rewarding work. The federal tax code currently taxes about 5.8 million low-wage workers aged into or deeper into poverty, because the payroll and federal income taxes they pay exceed any EITC they receive. An obvious way to help avoid a bigger spike in poverty is to stop taxing people into poverty. The EITC expansion for these workers in the Heroes Act would benefit 15.4 million working childless adults and reduce the number of them whom the federal tax code taxes into, or deeper into, poverty by 96 percent. Taxpayers may be able to claim the child tax credit if they have a qualifying child under the age of 17. Part of this credit can be refundable, so it may give a taxpayer a refund even if they don’t owe any tax.
Although changing your W-4 now won’t affect your 2019 taxes, it’s still worth taking a look for next year. A W-4 is a common form that you typically fill out when you start a new job. You can claim allowances, including for kids, which will bring down the amount that’s withheld out of every paycheck. If you have an outside caregiver take care of your kids at home, you may need to pay the so-called “Nanny Tax.” Essentially, if you have a nanny, the IRS may view you as an employer, so you’ll need to file the appropriate paperwork and additional taxes. Thankfully, the IRS has quite a few breaks for parents that could help put extra money back in your pocket. “Dependents are worth a lot of valuable tax deductions and credits,” Lisa Greene-Lewis, certified public accountant and tax expert at TurboTax, tells CNBC Make It.
The Additional Child Tax Credit (actc)
Allowing her to use her 2019 income would eliminate that added income loss. To address this problem, policymakers should incorporate the look-back proposal that allows filers to use their income from either 2019 or 2020 when calculating their 2020 EITC, which would cost a modest $3 billion. And if policymakers do not make the Child Tax Credit fully available to children in low-income families irrespective of their parents’ earnings, families should have the same option with respect to the low-income component of the Child Tax Credit. The look-back proposal was included in the Heroes Act and in bipartisan, bicameral legislation introduced by Senators Brown and Cassidy (S. 3542), and Representatives Higgins and Kelly (H.R. 6762).
- It is the single most crucial of the Child Tax Credit changes at this time, as it would best target assistance to low-income families — who are especially vulnerable — and hence would also provide the most effective stimulus per dollar of cost.
- This amount is also indexed to inflation, so it will increase slightly each year.
- As your income increases, the amount you can claim continues to decrease until you can’t claim the credit at all.
- An obvious way to help avoid a bigger spike in poverty is to stop taxing people into poverty.
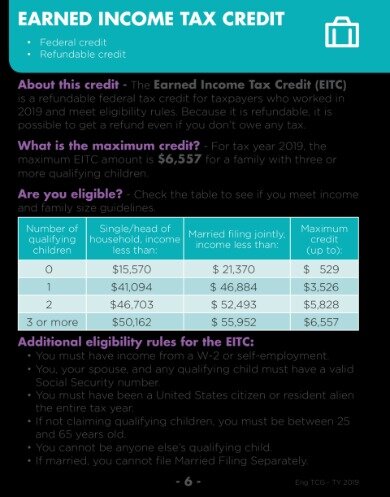
If you find discrepancies with your credit score or information from your credit report, please contact TransUnion® directly. Earned Income Tax Credit is specifically designed to benefit working people with low incomes. The percentage of allowable expenses decreases for higher-income earners — and therefore the value of the credit also decreases — but it never disappears completely.
Cbo Finds Expanding Eitc And Child Tax Credit Provides Effective Stimulus
Almost three-quarters of the benefits from making the CTC fully refundable would go to families with children in the bottom one-fifth of the income distribution. Senator Mitt Romney proposed a similar increase to the child tax credit last week, but created a permanent increase of $3,000 a year per child for school-aged children and $4,200 per child under 6. DeLauro’s office projects that the increase to the child tax credit, if implemented on a permanent basis and with a higher income cap as she has proposed, would cut overall childhood poverty by 45% in the U.S. The Democrats’ new proposal would increase the credit amount by $1,000 ($1,600 for those with children under 6) and allow taxpayers to receive the full amount as a refund. Additionally, the plan would make the credit payable in monthly installments of $250 and $300, respectively, rather than just once a year. The payments would start to phase out for individuals earning more than $75,000 a year or $150,000 for those married filing jointly. Moreover, policymakers need to take strong action to prevent the current sharp economic decline from causing poverty to spike dramatically, and one way to help do that would be to stop taxing people into — or deeper into — poverty.
Although the increase would be temporary, some lawmakers want to see a permanent boost put in place to dramatically reduce child poverty in the U.S. More recently, the CARES Act created an analogous relief mechanism for businesses. It not only allows businesses to deduct interest expenses equal to up to 50 percent of their adjusted taxable income but also gives them the option of using their 2019 income to make this calculation. Because of the recession, many businesses will have much smaller taxable incomes in 2020 than 2019, so using their larger 2019 income will let them deduct more in interest expenses and therefore obtain larger tax refunds. Policymakers should now extend this kind of option to hard-pressed working families as well. Providing this choice would be sound fiscal policy and provide important income insurance to families hurt by this deep downturn by ensuring that people don’t receive a smaller credit if their earnings fall in the current year due to the disaster.
Eligible families can claim a tax credit – which reduces income taxes they owe dollar-for-dollar – of up to $2,000 per child under age 17 who is a citizen of the U.S. The size of the credit is reduced by $50 for every $1,000 of adjusted gross income above $200,000 for single parents and $400,000 for married couples. The Child Tax Credit, which has been expanded significantly by Congress since it was first written into law nearly 25 years ago, is a significant element of the federal government’s effort to aid families with children. Families currently are eligible for a tax credit of up to $2,000 per child under age 17. President Biden proposes to expand the credit, which would, if Congress goes along, substantially reduce the number of children living below the poverty line. The IRS offers child tax credits to help parents and guardians offset some of the costs of raising a family. If you have a dependent who isn’t your direct child, you may also be eligible to claim a credit.
If your tax is $0 and your total earned income is at least $2,500, you can claim the refundable part of the credit, see the Additional Child Tax Credit section below. If Congress makes the credit fully refundable but leaves the maximum credit at $2,000 per child under 17 , it could reduce the annual cost of the CTC expansion to about $24 billion. That’s because most middle- and high-income families already receive the full $2,000 CTC.
Is The Irs Up For The Challenge?
Making the Child Tax Credit fully available would lift more than 3 million people — including 2 million children — above the poverty line. It would lift another 13.6 million poor people, including 6.8 million children, closer to the poverty line. And for more than 1 million of these people, including 770,000 children, the expansion would lift them out of deep poverty by raising their income above half of the poverty line. By increasing the purchasing power of very poor families, this also would be highly effective economic stimulus, since these hard-pressed families will spend virtually all of any additional income they receive. A number of states offer some version of an earned income tax credit for working families, so you might be able to get that credit, too. The Child Tax Credit is one of three kid-focused federal tax credits that are among the most effective ways to reduce your tax bill.
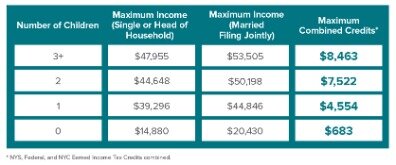
Tax credits can dramatically reduce what you owe the IRS or boost your tax refund – here’s what you need to know. Expanding the credit has been popular with both Democrats and Republicans in part because assisting low-income and middle-class families with children is regarded by members of Congress as both politically appealing and economically prudent. You may go back up to four years to claim CalEITC by filing or amending a state income tax return.
How To Qualify For The Child Tax Credit
People whose incomes fall this year, making them newly eligible for the EITC during the downturn, could use their 2020 income, as under current law. But lower-income workers who lose a job or have their hours and earnings cut could use their 2019 income to avoid losing some or all of their EITC. CBO’s latest economic and budget projections show that the unemployment rate will remain above 10 percent through the end of the year and that it won’t return to the levels in CBO’s pre-pandemic economic projections until late in the decade.
This will amount to $117.5 billion for qualifying families – twice the amount provided by the Earned Income Tax Credit, a program which supplements the wages of low-paid workers. similar to Biden’s plan by offering a monthly amount for children — $300 for a child under 6 years old and $250 for a child between the ages of six and 17. Some savings options, like a health savings account, dependent care or health care flexible spending account or 401, allow you to contribute pre-tax money. With a dependent care FSA, that means you are not paying taxes on contributions that you then spend on dependent care. This decreases your taxable income and could potentially drop you into a lower tax bracket. Even if your contributions didn’t change your bracket in the past, make sure to check thecurrent tax brackets. They may have changed since you last filed, so contributing slightly more might now help you to really boost your savings.
Republicans first proposed the CTC back in 1997 as part of the Taxpayer Relief Act. And it was Sen. Marco Rubio, a Republican from Florida, who spearheaded the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 that doubled the credit from $1,000 to its current amount. Democratic support for a tax credit created by Republicans makes a bipartisan plan for expanding the credit more likely.
So, when you breach a certain income threshold (the phase-out level), you’re only eligible for a partial credit. As your income increases, the amount you can claim continues to decrease until you can’t claim the credit at all. When you prepare your tax return on eFile.com, we will automatically check to see if you qualify for the Child Tax Credit. If you qualify for the credit, the exact amount will be calculated for you.
Some states offer a complementary state-level CTC and/or CDCTC that matches part or all of the federal credit. In some states, the credits are refundable and in other states they are not.This state-by-state guide breaks down which states offer their own Earned Income Tax Credit, CTC or CDCTC. Only one taxpayer may claim any one child for the purposes of the Child Tax Credit and the Additional Child Tax Credit. If a child is claimed as a dependent on more than one tax return, the IRS will determine who gets the claim according to a set of tiebreaker rules. There are factors to consider when it comes to a child or children and income taxes. The HEROES Act would temporarily increase the average CTC benefit for families with children by $2,260, boosting benefits for almost 90 percent of families with children. The Joint Committee on Taxation estimates the expansion would cost just under $109 billion in fiscal year 2021.
Claim Your Credit
Families who owe little or no income tax can get cash of up to $1,400 per child, a feature which makes the tax credit partially “refundable,” in the jargon of Washington. If you qualify for CalEITC and have a child under the age of 6 as of the end of the tax year, you may qualify for up to $1,000 through this credit. Generally, because when taxes are refunded to families, they tend to spend it. For the bottom 20% of families in terms of income, the proposed expansion of the CTC would increase income by an average of 9.7% — even higher if you only consider tax filers with children, according to the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy.

