Content
The Fed also raises interest rates to help offset the risk of inflation in a growing economy near full employment. However, as the tax plan became clearer and its impact on the economy was judged to be relatively minor, the Fed indicated that a plan to raise interest rates incrementally as many as three times in 2018 would not be changed. During 2019, income groups earning under $20,000 (about 23% of taxpayers) would contribute to deficit reduction (i.e., incur a cost), mainly by receiving fewer subsidies due to the repeal of the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act.
In addition, a tax deduction is now disallowed entirely for charitable contributions if the donor receives rights to receive seats to college athletic events. Formerly, 80% of the charitable contribution was considered to be a tax-deductible charitable contribution. There is a 1.4% excise tax on investment income of certain private tax-exempt colleges and universities. The excise tax applies only if the institution has at least 500 tuition-paying students and more than half the students are located in the United States. There is a 25% excise tax on compensation paid to certain employees of churches and other tax-exempt organizations.

Netting the unrelated business income from transportation with other unrelated business income in order to reduce or eliminate the amount of tax due is allowed. Unrelated business income is now increased by the amount a church or other tax-exempt organization pays or incurs for qualifying parking or qualifying transportation benefits for its employees. This type of unrelated business income includes only tax-free transportation benefits provided to employees, not transportation benefits that are included in the employee’s taxable wages. The law also eliminated the net operating loss carryback, an procedure by which a company with significant losses could receive a tax refund by counting the losses as part of the previous year’s tax return. They were considered important in providing liquidity during a recession. The provision was cut in order to finance the tax cuts in the act, and was one of the largest offsets in the law. Don’t wander into the 2020–2021 federal income tax seasons wondering what you’ll owe Uncle Sam.
How The Tax Reform Bill Impacted Your Taxes
A larger exemption for the estate tax will benefit you if you leave an estate that’s worth a lot of money. The TCJA doubled theestate taxexemption from $5.6 million in 2017 to $11.2 million in 2018. The Tax Foundation has indicated that those who earn more than 95% of the population will receive a 2.2% increase in after-tax income. Those in the 20% to 80% range would receive a 1.7% increase.
And for low- and moderate-income families, it means the maximum EITC will increase more slowly. By 2027, a married couple making $40,000 with two children will see their federal EITC shrink by $283 in 2027 (from $5,025 to $4,742). For example, those budgets have consistently featured large cuts in Medicaid, which provides health and nursing home care to millions of these families. Low- and moderate-income Americans should not now be left holding the tab for tax cuts tilted to the top, through cuts to, or underinvestment in, critical priorities. Instead, lawmakers can reverse course and raise substantially higher progressive revenues to meet national challenges.
Fewer Households Will Incur Alternative Minimum Tax Liability
The act doubles the estate and gift tax exemption for estates of decedents dying and gifts made after Dec. 31, 2017, and before Jan. 1, 2026. The basic exclusion amount provided in Sec. 2010 increased from $5 million to $10 million and will be indexed for inflation occurring after 2011.
With the likely outcome of the tax cuts being increased debt, it’s important to understand how that debt affects the GDP. The World Bank estimates that for every percentage point that a nation’s debt-to-GDP ratio increases above 77%, that nation’s GDP will decrease by 1.7%. The Tax Foundation made a slightly different estimate. The tax cuts themselves would cost $1.47 billion but savings from eliminating the ACA mandate and GDP growth would offset that figure by $700 billion. The plan would boost gross domestic product by 1.7% a year, create 339,000 jobs, and add 1.5% to wages. The adoption of elements of territorial taxation allows companies to repatriate the approximately $1 trillion they hold in foreign cash stockpiles.
Experts say that the financial windfall for the President and his family from this bill is “virtually unprecedented in American political history”. The finance ministers of the five largest European economies wrote a letter to U.S. Treasury Secretary Steve Mnuchin, expressing concern that the tax reforms could trigger a trade war, as they would violate World Trade Organization rules and distort international trade. In response to the Act, German economists called for the German government to enact tax reform and additional subsidies to prevent a loss of jobs and investments to the United States. The top 1% of households by wealth own 40% of stocks; the bottom 80% just 7%, even when including indirect ownership through mutual funds. U.S. corporate profits after-tax from 1970 to Q2 2017.
The rushed approval of the legislation prompted an outcry from Democrats. Senate Minority Leader Charles Schumer (D–NY) proposed giving senators more time to read the legislation, but this motion failed after every Republican voted no.
- There is a lengthy bipartisan history of exempting from the cap certain types of program integrity funding — to reduce errors, overpayments, and fraud in government programs and taxes — that OMB estimates will produce net savings.
- Analysts attributed the fiscal 2018 decline to the tax cut.
- This means that a taxpayer may be able to claim this credit for children age 17 or over, including college students, children with ITINs, or other older relatives in the household.
- The top 1 percent of households will get 61 percent of this tax cut on pass-through income in 2024, while the bottom two-thirds of households will see just 4 percent, according to JCT.
- However, taxpayers 65 and older are able to use a previous threshold of just 7.5% of their AGI when itemizing and taking a deduction in 2016.
The IRS has estimated that the average time to complete an individual tax return will decrease by 4 to 7 percent. This would reduce the time of 15 hours spent filing Form 1040 to an average between 13.95 and 14.4 hours per Form 1040. If we expect 150 million individual income tax filers, this translates into a total time savings anywhere from 90 million to 157.5 million hours. Converting this to dollar terms, savings could range from $3.1 billion to $5.4 billion.
The act exempts the discharge of certain student loans due to the death or total permanent disability of the borrower from taxable income. This provision applies only to debt discharged during tax years 2018 through 2025. Take back your hard-earned cash and pay the IRS only what you have to. Use this free quiz to help you decide which tax filing method is right for you.
Yet estimates from CBO that take into account the law’s macroeconomic impact as well as increase in interest payments on the added debt still put its cost at $1.9 trillion. Any budget deal should include adequate funding of the IRS, and particularly for IRS enforcement. IRS enforcement funding overall has been cut by 25 percent since 2010, after adjusting for inflation, and the enforcement division has lost roughly 30 percent of its workforce over that period.
The rate for medical and moving mileage drops to 17 cents per mile, down from 19 cents. The charitable mileage rate remains at 14 cents per mile. File with a tax Pro At an office, at home, or both, we’ll do the work. Taxpayers should review their tax withholding in 2019 and make any adjustments with their employer as early in the year as possible. This can help protect against having too little tax withheld and facing a lower refund or unexpected tax bill and even a penalty next year. Adds $1.9 trillion to deficits over 2018 to 2027, putting pressure on critical economic security programs and investments.
Republicans justified the tax reform initially as an effort to simplify the tax code. Kevin Brady, the chairman of the House Ways and Means Committee, and Speaker Paul Ryan said in November 2017 that they would simplify the tax code so much that 9 in 10 Americans would be able to file their taxes on a postcard. President Donald Trump said on December 13, 2017, that people would be able to file their taxes “on a single, little, beautiful sheet of paper”. However, when the final version of the tax legislation passed through houses of Congress, the legislation kept most loopholes intact and did not simplify the tax code.
Standard Deduction
Significant tax benefits would only accrue to the top 20% of taxpayers. Income of households in the bottom 99% percent would be higher than at any time in the past, adjusted for inflation, also continuing previous trends. The third quintile (taxpayers in the 40th to 60th percentile with income between $48,600 and $86,100, a proxy for the “middle class”) would receive 11% of the benefit in 2018 and 2025, but would incur a net cost in 2027. The top 1% of taxpayers (income over $732,800) would receive 8% of the benefit in 2018, 25% in 2025, and 83% in 2027. In a November 2017 survey of leading economists, only 2% agreed with the notion that a tax bill similar to those currently moving through the House and Senate would substantially increase U.S.
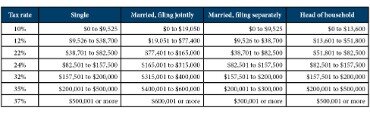
But, if your total itemized deductions don’t exceed Trump’s higher standard deduction, you won’t be able to take it. The biggest changes under the new Trump tax plan came for those in the middle of the chart. A married couple whose total income minus deductions is $250,000, for instance, would have had a tax rate of up to 33% in 2017.
It doubled the maximum per child credit amount from $1,000 to $2,000 starting in 2018. It also increased the refundable portion of the credit but limited the maximum refundable credit to $1,400 per child in 2018.
The [pass-through] deduction leaves a gaping hole in the tax code, and the goal by the end of the presentation today is to make you guys the bus drivers, or the truck drivers, to drive right through that hole with your clients. As a 501 nonprofit, we depend on the generosity of individuals like you. Help us continue our work by making a tax-deductible gift today.
Tax Services
See the 2018 Instructions for Form 6251PDF, Alternative Minimum Tax – Individuals for more information. Beginning with tax year 2018, a child must have a Social Security number issued by the Social Security Administration before the due date of the tax return to be claimed as a qualifying child for the child tax credit or additional child tax credit. Children with an ITIN can’t be claimed for either credit. Taxpayers who pay too much tax during the year will claim a credit or refund for the overpayment while those who have too little tax, either through withholding or paid through estimated payments, may owe tax. Retains and creates incentives for companies to shift profits and investment offshore, which risks weakening workers’ wages.
The 2017 tax law repealed the Affordable Care Act’s requirement that most people enroll in health insurance coverage or pay a penalty. In 2019 alone, eliminating that penalty will raise the number of uninsured by 4 million and raise premiums in the individual insurance market by about 10 percent, according to the Congressional Budget Office . Risks harming workers’ wages and workplace standards due to its pass-through deduction. The law’s 20 percent deduction for pass-through businesses is overwhelmingly tilted to the highest-income filers. My colleagues have also explained that the deduction may fuel a move towards “fissured workplaces,” because it creates an incentive for firms to buy workers’ services without employing them directly. Examples include hiring workers as “independent contractors” instead of as employees, or by hiring workers through another firm .
million fewer persons covered by health insurance as some younger, healthier persons will likely choose not to participate. Those in the remaining less healthy pool will pay higher insurance costs on the ACA exchanges, which will result in additional persons dropping coverage. The Act contains provisions that would open 1.5 million acres in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge to oil and gas drilling. This major push to include this provision in the tax bill came from Republican Senator Lisa Murkowski. The move is part of the long-running Arctic Refuge drilling controversy; Republicans had attempted to allow drilling in ANWR almost 50 times. Opening the Arctic Refuge to drilling “unleashed a torrent of opposition from conservationists and scientists.” Democrats and environmentalist groups such as the Wilderness Society criticized the Republican effort.
The standard deduction nearly doubles, from $12,700 to $24,000 for married couples. For single filers, the standard deduction will increase from $6,350 to $12,000.

