Content
Often, shareholders do not track the impact of these distributions properly. Every dollar of non-dividend/liquidating distribution reduces the basis in an investment. After the basis is reduced to zero, any additional non-dividend distributions are treated as capital gain. Investment companies or advisors may track basis for the shareholder, but often the basis tracking is not done unless done by the taxpayer. On the contrary, dividends issued by REITs are generally excluded from unrelated business taxable income.

A taxpayer that elected out of the 163 limitation may claim bonus depreciation on personal property and depreciate its qualified improvement property placed in service after December 31, 2017 over a shortened (20-year) recovery period. A REIT that allows a tenant to defer paying rent will continue to accrue and recognize that rental income, and therefore will have to take that income into account for the 90% dividend distribution requirement, even though the REIT has not received a corresponding cash payment. There are several options available to REITs to address this mismatch, discussed below.
Rents from real property is defined to include rents; charges for services customarily furnished in connection with rental of real property; and generally rent attributable to personal property which is leased in connection with a lease of real property. Impermissible tenant service income is excluded from rents from real property.
Real Estate And Construction Industry Outlook
He holds a Bachelor of Arts degree in Economics and International Studies from Yale University, and a Masters of Business Administration degree from the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for, tax, legal or accounting advice. If you’re not satisfied, return it within 60 days of shipment with your dated receipt for a full refund (excluding shipping & handling).
Shareholders who fall into the highest income tax bracket, which is currently 37%, will pay 20% for long-term capital gains. This occurs when the company sells one of its real estate assets and realizes a profit. Nareit® is the worldwide representative voice for REITs and publicly traded real estate companies with an interest in U.S. real estate and capital markets. Nareit’s members are REITs and other businesses throughout the world that own, operate, and finance income-producing real estate, as well as those firms and individuals who advise, study, and service those businesses. National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts® and Nareit® are registered trademarks of the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts . This occurs when the REIT sells property it has held for at least one year.
Marcum LLP is a top-ranked national accounting and advisory services firm dedicated to helping entrepreneurial, middle-market companies and high net worth individuals achieve their goals. Marcum offers industry-focused practices with specialized expertise to privately held and publicly registered companies, and nonprofit and social sector organizations. By reporting incorrect numbers in the last two columns, the shareholder ends up reporting too much or too little income and is either incurring significant audit risk or too much tax. Every individual and company takes a different approach to understanding and complying with their tax obligations. This can impact both total tax liability and potential audit risk. However, REITs’ unique tax structure creates important considerations when determining the optimal tax strategy. CNBC quoted MidAtlantic Regional Tax Partner-in-Charge Edward Reitmeyer in an article about the Supreme Court ruling forcing the disclosure of former President Donald Trump’s tax returns to New York investigators.
The remaining $0.60 comes from depreciation and other expenses and is considered a nontaxable return of capital. If the last day of either the 45-day period to identify replacement property for a section 1031 like-kind exchange or the 180-day period to close on replacement property falls on or after April 1, 2020 and before July 15, 2020, then the applicable period is extended to at least July 15, 2020. More information about the COVID-19-related tax credits available to employers under the FFCRA, including how to obtain the credits, is available here. A REIT may amend its existing credit facilities to defer payments. However, if the amendment constitutes a “significant modification,” the REIT may recognize “cancellation of indebtedness” income. The Treasury Regulation also outlines certain safe harbors for alterations that will not be treated as significant modifications. This includes a safe harbor for forbearance of debt collection for a period of two years , as well as any additional period during which the parties conduct good faith negotiations or during which the issuer is in a title 11 bankruptcy or similar case.
Section 501 tax-exempt organizations are eligible for the credit, but governmental entities and companies receiving loans under the CARES Act as part of the Small Business Administration’s Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP”) are not. If a company receives a PPP loan, all other persons that are treated as one employer with that company under the rules described above are ineligible for the credit. The operation of an employer’s trade or business is “partially suspended” due to a governmental order related to COVID-19 if the employer is able to “continue some, but not all of its typical operations” as a result of the governmental order.
The CARES Act allows corporate taxpayers that may be able to carryback losses a 120-day period to make certain important elections, including the election to forego the carryback. A REIT that holds multifamily properties with a federally backed mortgage loan may be able to take advantage of provisions under the CARES Act that require servicers of those loans to grant forbearance on collection.
Myth 3: Reits Are Exclusively Income
For example, if an apartment-building REIT overestimates demand and rent levels, the REIT owning it could end up losing money on the investment, at least in the short term. But residential REITs tend to own portfolios of real estate purchased at different times. Many direct real estate investors assume that values will rise over time, but this is by no means guaranteed. And even if this happens, the gain before sale might not be enough to compensate for a potential disparity between long-term income and cumulative costs. In this scenario, contrary to what the investor expected, there would be no long-term profit. Like stocks, they’re bought and sold on major exchanges throughout the trading day.
The act gives a new 20% deduction for pass-through business income, which includes qualified REIT dividends. If a governmental order requires an employer to close its workplace for certain purposes, but the workplace may remain operational for limited purposes, is the employer considered to have a suspension of operations? However, a software company is not considered to be partially suspended if it closes its office in accordance with a citywide order closing all non-essential businesses, but is able to continue operations comparable to its operations prior to the closure by having its employees work remotely.
The average dividend yield for REITs was about 4.3% in September 2012, well more than the yield of the S&P 500 Index, but pretty far below the longer-term average for REITs, which had been trending in the 7%-8% range . Also, REIT dividends are secured by stable rents from long-term leases, and many REIT managers employ conservative leverage on the balance sheet. You may use TurboTax Online without charge up to the point you decide to print or electronically file your tax return.
- The downside is, if the plan of liquidation is not completed within two years, the shareholders must go back and report everything as it would have been, absent the plan of liquidation adding tax and penalty into the mix.
- These will normally be taxed at your regular income tax rate, the same as wages from a job, unless a portion or all of them are “qualified dividends”.
- The CARES Act corrects an error in the TCJA that prevented businesses from expensing certain costs for improvements to “qualified improvement property,” and required the costs to be depreciated over the 39-year life of the building.
- Capital gains distributions, for example, are subject to capital gains taxes.
- However, they can encounter problems resulting in losses being passed on to investors in the form of pummeled share value.
- While the allure of not paying taxes is attractive, REITs may not be the best vehicle for an individual who directly owns property.
This is because the employee would be unable to work even if he or she were not required to comply with the quarantine or isolation order. If a governmental order requires non-essential businesses to suspend operations but allows essential businesses to continue operations, is the essential business considered to have a full or partial suspension of operations? If a governmental order causes the customers of an essential business to stay at home is the essential business considered to have a suspension of operations?
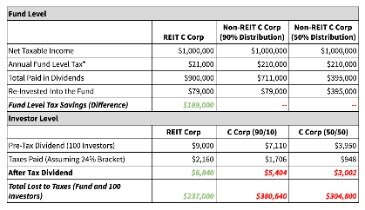
The shareholders simply recognize dividend income and pay tax in their state of residence. The presence of a REIT is very attractive to tax-exempt investors. While these investors are generally exempt from paying federal tax by definition, many may still be subject to unrelated business income tax on their share of debt-financed real estate income. Real estate investment trusts, like many companies, distribute earnings to investors in the form of dividends. Unlike many companies however, REITs are not taxed at the corporate level. That means REITs avoid the dreaded “double-taxation” of corporate tax AND personal income tax. Instead, REITs are sheltered from corporate tax so their investors are only taxed once.
There is no cap on the deduction, no wage restriction, and you do not need to itemize deductions to receive this benefit. These forms properly breakdown the ratio of taxable to non-taxable dividend payments, as well as the method used by management to calculate the return-of-capital percentage.
However, under a second Sun Capital case, where a single sponsor managed two funds that did not invest in parallel, the holdings of the two funds were not aggregated. Finally, section 414 contains special rules for “affiliated service groups”. A REIT may need to modify leases or defer rent payments for a third-party tenant that is unable to meet its rent obligations. Generally, as long as a lease is not treated as a debt instrument for U.S. federal income tax purposes, modifications of the lease should not give rise to a taxable event. However, if the legal rights and obligations that are altered under the lease and the degree to which they are altered are “economically substantial,” the lease will need to be re-tested to determine whether it is a section 467 lease. A section 467 lease generally is a lease with respect to which the total amount of payments that the lessor receives for use of the leased property is greater than $250,000, and that has increasing, decreasing, prepaid, or deferred rents. If a modification to the lease does result in a REIT holding a section 467 lease, it could affect the character and timing of the REIT’s income recognition, which could in turn impact a REIT’s ability to meet its required income and distribution requirements.
Asset And Income Tests
Thus, the REIT inadvertently subjects its shareholders to higher tax rates and earlier tax payment, though both could have been avoided with better planning. The downside is, if the plan of liquidation is not completed within two years, the shareholders must go back and report everything as it would have been, absent the plan of liquidation adding tax and penalty into the mix. When taxpayers do not track basis, it can cause a dilemma later when a shareholder sells an investment or the investment is redeemed in liquidation. A shareholder who fails to track basis must either gather the information for all the prior years the investment was held, or make a simplifying assumption. Depending on how long the investment was held, retroactively recreating the basis may be time-consuming or even impossible.
However, the employer may continue to defer any payroll tax that it deferred prior to the loan forgiveness in accordance with the CARES act rules. No excise tax is imposed on a REIT that makes a spill-over dividend. Let’s assume a REIT liquidates on January 15 of year 3, on schedule as planned on January 15 of Year 1. Let’s further assume that the REIT has $1000 of ordinary income during years 1 and 2, and none in year 3. Let’s also assume that the amount of capital gain the REIT realizes upon liquidation of all its assets in year 3 is the same as the shareholders’ initial investment and equals the amount of cash available at the time of liquidation. Well-managed REITs do not pay federal tax and avoid most state taxes, as well. Consequently, REITs may operate under the premise that REIT status automatically generates the best case tax scenario for shareholders.
Ordinary Dividend – Prior to the TCJA, any 199A income was reported as ordinary income. Now, an ordinary dividend on your 1099-DIV from a REIT that is not also reported as a 199A or qualified dividend is a trigger to make sure that the 1099-DIV is correct. This is to say, if you get a 1099-DIV from a REIT and the combination of box 1b and box 5 does not equal box 1a, you should probably make sure an error hasn’t been made. However, they can encounter problems resulting in losses being passed on to investors in the form of pummeled share value. Most REITs are publicly traded like stocks, making them highly liquid — unlike most real estate investments. As an investment, REITs have long had advantages over owning property directly.
All persons treated as a single employer under section 52 or or section 414 or are treated as one employer for all purposes of the credit, including for purposes of determining whether they exceed the 100 full-time employee threshold. First, companies related through greater than 50% ownership are treated as one employer for purposes of the 100 full-time employee threshold. Second, chains of organizations conducting trades or businesses may be treated as one employer if they are common control. Therefore, under the court’s holding, two corporations more than 50% of the vote or value of each of which is owned by a private equity fund would be treated as a single employer for purposes of the 100 full-time employee rule. In Sun Capital, the court treated parallel funds as one entity for tax purposes where the funds were run by the same sponsor, shared a single general partner, and invested nearly identically. Therefore, under Sun Capital, if two parallel funds each own 50% or less of two corporations, but the funds in the aggregate own more than 50% of each corporation, both corporations would be treated as a single employer.
When the shares are eventually sold, the difference between the share price and reduced tax basis is taxed as a capital gain. The dividend payments that REIT investors receive can constitute ordinary income, capital gains, or a return on capital.
Conditions Ripe For Strategic Real Estate, Construction Investments
A plan of liquidation can last two years prior to liquidating a REIT, which means the impact of the plan of liquidation can appear on up to three years of the REIT shareholders’ tax returns. 199A Dividend – This dividend type is new thanks to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 .

